The world today is flooded with flash products, you can find them everywhere in many products.
Some examples for Flash drives:
- USB drive (Disk on key).
- Digital Camera Memory cards of all types(SD, MMC, microSD etc.)
- SSD drives – solid state hard drives.
- Pen Cameras.
- Sound Recorders.
- Smart Phones.
Known faults of Flash Media which can cause data loss:
- Firmware/Tables corruption – each flash device has embedded software that is responsible for its activity. When this software gets corrupted it will not work properly and most times will ask to reformat the media.
- Bad connections – since most of these devices are potable they may experience physical damage to the connections – USB connector disconnected, bad soldering etc.
- Failing PCB(printed circuit board) – as most of these products are dirt cheap today, quality is not high and some of the components may fail, mainly the controller.
- Physical Damage – device was crushed physically, people sat on it, car ran it over etc.
- Accidental Format/Files Deletion – in this case the physical media is not faulty. The user accidentally formatted flash media or deleted files.
What is flash Technology
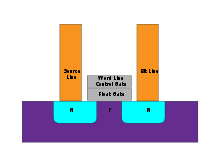
Flash cell structure
As described in the image above, data on flash technology is saved in many cells (single cell description in image below). Electrons are saved in the cyan/blue area to form a value of 1 or 0. The data is saved in an electronic way. Millions of cells are stored in every flash chip to form a storage unit like a USB disk for example. On legacy hard drives there are electro-mechanical mechanisms and data is saved as magnetic value which represents 1 and 0.
Pros for using Flash: more resistant to physical damage, falls, weather etc.
Cons for using Flash: limited number of cells writes – cell will die after 5000-10,000,000 number of writes.

- flash chip
The image above shows a common flash chip which is embedded in all the devices mentioned at the start of the page.

USB Flash Drive
This is an example of an open USB disk, it is easy to see the flash chip inside (large one), the smaller chip is the controller (processor).

- SSD data recovery IT LAND
This is an example of an open SSD (solid state drive), it is easy to see a lot of flash chips inside (larger capacity).
We provide Data Recovery & Forensic Services Australia wide to:
Gold Coast, Tweed Heads,Byron Bay, Ballina, Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Adelaide, Darwin, Newcastle, Canberra, Queanbeyan, Wollongong, Sunshine Coast, Hobart, Geelong, Townsville, Cairns, Toowoomba, Launceston, Albury, Wodonga, Ballarat, Bendigo, Mandurah, Mackay, Burnie, Devonport, Latrobe Valley, Rockhampton, Bundaberg, Bunbury, Hervey Bay, Wagga Wagga, Coffs Harbour, Gladstone, Mildura, Shepparton, Tamworth, Port Macquarie, Orange, Dubbo, Geraldton, Nowra, Bomaderry, Bathurst, Warrnambool, Lismore, Kalgoorlie, Boulder and more.
